friendly diamonds
INR
- Engagement RingsEngagement Rings
Create your own
pre-designed engagement rings
Shop by style
Shop by metal
- Back
The Gemological Institute of America (GIA ) established the 4 C's as the fundamental criteria for assessing diamond quality on a global scale. These factors, including Cut, Colour, Clarity and Carat, play a pivotal role in determining both the visual appeal and value of a diamond.
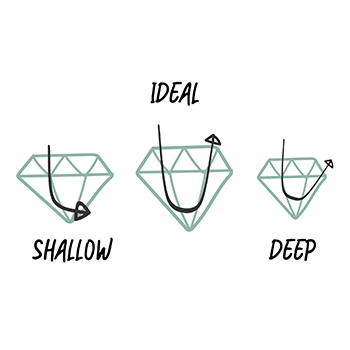
Contrary to a common misconception, a diamond's cut isn't solely about its shape; it involves how its facets interact with light. This interaction allows light to pass through, creating the sparkle that defines a diamond. A skilled craftsman meticulously cuts a diamond to ensure proper proportions and symmetry, with excellent and very good cuts delivering exceptional brilliance. A good cut strikes a balance between quality and value, while a fair cut may exhibit light leakage and a poor cut leads to significant dullness.

Diamond weight is measured in carats, where one carat equals 200 milligrams. This standardized unit facilitates the accurate measurement of a diamond, not just indicating how big a diamond appears but actually reflecting its total weight. While larger diamonds usually have higher carat weights and are often considered more valuable because of their size, it's important to understand that a diamond's quality and beauty aren't solely defined by carat. Other factors also play a role in its overall visual appeal.
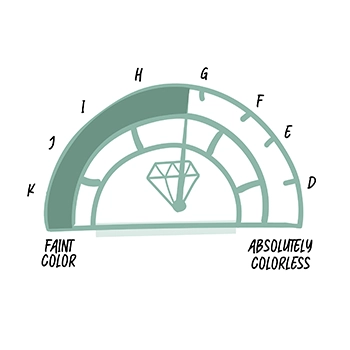
A diamond's colour is influenced by trace impurities in its crystal lattice, impacting its appearance and value. Lab diamonds come in various colours, such as colourless, near colourless, faint yellow, light yellow and brown. The Gemological Institute of America (GIA) grades diamond colour on a scale from D (colourless) to Z (light yellow or brown). However, D is a higher colour grade, which indicates less colour and greater value. Whereas Z is the lowest colour grade, which indicates more colour and a lesser value.

Clarity measures the purity of a diamond by assessing inclusions (internal imperfections) and blemishes (external imperfections). The clarity scale ranges from Fl (flawless) to I3 (included). A flawless diamond (FI) exhibits no inclusions or blemishes visible to the naked eye, even under 10x magnification. In contrast, an I3 diamond has numerous visible inclusions and blemishes.
Friendly Diamonds introduces two more C's – Certification and Conscience – shedding light on the authenticity and social impact of each diamond. These aspects play an important role in guiding buyers towards making well-informed and socially responsible purchases.

The GIA developed a certification system to evaluate diamond quality based on the 4 C’s—carat, colour, clarity and cut. Diamond certifications furnish buyers with detailed information about a diamond's characteristics, aiding informed purchase decisions. Additionally, certifications ensure diamonds are authentic and comply with international standards.

Lab diamonds offer a compelling solution to the ethical concerns entangled with traditional mining practices in the diamond industry. Opting for lab grown diamonds represents a conscious choice to embrace a gem with a humane origin, untethered from the ethical shadows that have often plagued the conventional diamond trade.